A C-program is a set of instructions. Just like a recipe - which contains instructions to prepare a particular dish.
Types of instructions:
1.Type declaration instruction
2. Arithmetic instruction
3.Control instruction
Note:
1.No operator is assumed to be present
int i=ab ( Invalid )
int i=a*b ( valid )
2.There is no operator to perform exponentiation in c however we can use pow(x,y) from <math.h>(More later).
Note:
1.No operator is assumed to be present
int i=ab ( Invalid )
int i=a*b ( valid )
2.There is no operator to perform exponentiation in c however we can use pow(x,y) from <math.h>(More later).
Quick Quiz:
Question- int k=3.0/9 value of k? and why?
Solution- 3.0/9=0.333 but since k is an int, it cannot store floats & value 0.33 is demoted to 0.
Operator Precedence in C
3*x-8y is (3x)-(8y) or 3(x-8y)?
In c language, simple mathematical rules like BODMAS no longer applies.
The answer to the above question is provided by operator precedence & associativity.
Operator precedence
The following table list the operator priority in C
| Priority | Operators |
| 1st | * / % |
| 2nd | + - |
| 3rd | = |
Operators of higher priority are evaluated first in the absence of parenthesis.
Operator associativity
When operators of equal priority are present in an expression, the tie is taken care of by associativity
x * y / z => (x * y) / z
x / y * z => (x / y) * z
*, / follows left to right associativity.
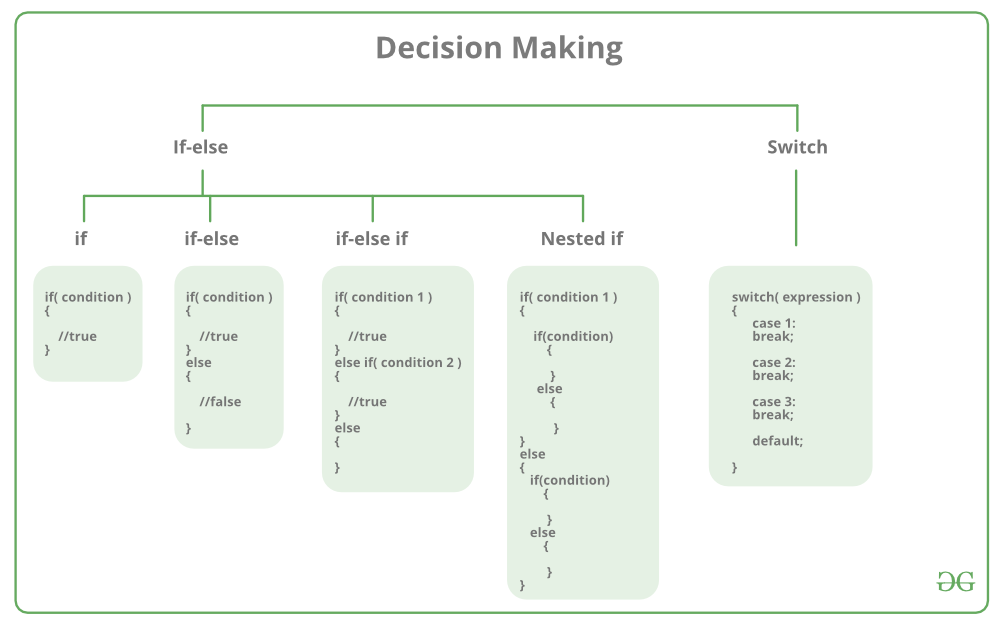
Control instructions
Determines the flow of control in a program.
Four types of control instruction in C are:
1. Sequence Control Instruction
2. Decision Control Instruction
3. Loop Control Instruction
4. Case-Control Instruction
No comments:
Post a Comment