In ‘C’ language, we must be able to execute instructions on a condition(s) being met.
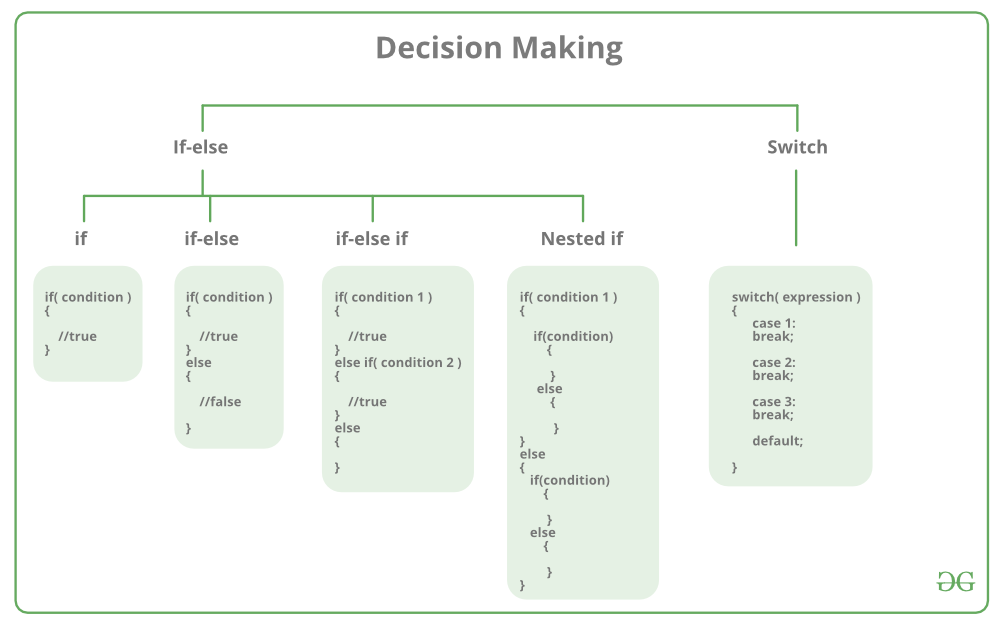
Decision making instructions in C
- If-else statement
- Switch statement
If-else statement
The syntax of an if-else statement in c looks like:
if ( condition to be checked) {
Statements-if-condition-true ;
}
else{
statements-if-condition-false ;
}
Code Example
Note that else block is not necessary but optional.
Relational Operators in C
Relational operators are used to evaluate conditions (true or false) inside the if statements. Some examples of relational operators are:
| == | equals to |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| > | greater than |
| < | less than |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| != | not equal to |
Important Note: '=' is used for an assignment whereas '==' is used for an equality check.
The condition can be any valid expression. In C a non-zero value is considered to be true.
Logical Operators
&&, ||, and ! are the three logical operators in C. These are read as “and”, ”or”, and “not”. They are used to provide logic to our c programs.
Use of logical operators:
1. && (AND) is true when both the conditions are true
“1 and 0” is evaluated as false
“0 and 0” is evaluated as false
“1 and 1” is evaluated as true
2. || (OR) is true when at least one of the conditions is true. (1 or 0 = 1)(1 or 1 = 1)
3. ! returns true if given false and false if given true.
!(3==3) evaluates to false
!(3>30) evaluates to true
As the number of conditions increases, the level of indentation increases. This reduces readability. Logical operators come to rescue in such cases.
Else if clause
Instead of using multiple if statements, we can also use else if along with if thus forming an if-else if-else ladder.
if {
// statements ;
}
else if { //statements;
}
else { //statements;
}
Using if-else if-else reduces indents. The last “else” is optional. Also, there can be any number of “else if”.
Last else is executed only if all conditions fail.
Operator Precedence
| Priority | Operator |
| 1st | ! |
| 2nd | *,/,% |
| 3rd | +,- |
| 4th | <>,<=,>= |
| 5th | ==,!= |
| 6th | && |
| 7th | || |
| 8th | = |
Conditional operators
A shorthand “if-else” can be written using conditional or ternary operators.
Condition ? expression-if-true ; expression-if-false
Here, '?' and ':' are Ternary operators.
Switch case-control instruction
Switch-case is used when we have to make a choice between the number of alternatives for a given variable.
Syntax,
Switch(integer-expression)
{
Case c1:
Code;
Case c2: //c1,c2,c3 are constants
Code; //Code is any valid C code
Case c3:
Code;
default:
Code;
}
The value of integer-expression is matched against c1,c2,c3......if it matched any of these cases, that case along with all subsequent “case” and “default” statements are executed.
Quick Quiz: Write a program to find the grade of a student given his marks based on below:
90-100 A <70- F
80-90 B
70-80 C
60-70 D
Important notes
- We can use switch case statements even by writing in any order of our choice
- Char values are allowed as they can be easily evaluated to an integer
- A switch can occur within another but in practice, this is rarely done
- What will be the output of this program?
- Write a program to find out whether a student is pass or fail; if it requires a total of 40% and at least 33% in each subject to pass. Assume 3 subjects and take marks as an input from the user.
- Calculate income tax paid by an employee to the government as per the slabs mentioned below:
| Income Slab | Tax |
| 2.5L-5.0L | 5% |
| 5.0L-10.0L | 20% |
| Above 10.0L | 30% |
Note that there is no tax below 2.5L. Take income amount as an input from the user.
- Write a program to find whether a year entered by the user is a leap year or not. Take the year as input from the user.
- Write a program to determine whether a character entered by the user is lowercase or not.
- Write a program to find the greatest of four numbers entered by the user.
No comments:
Post a Comment